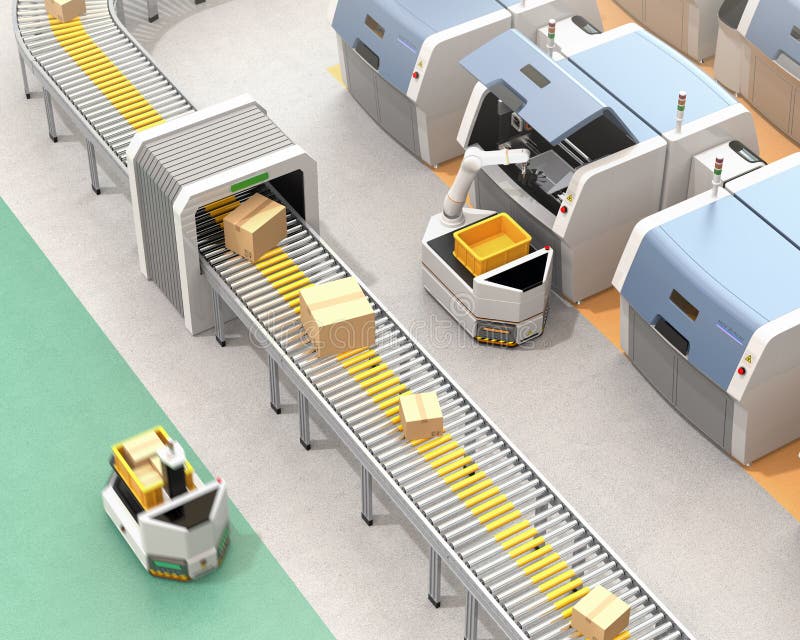
AGVs
All automated guided vehicle or automatic guided vehicle (AGV) is a mobile robot that follows markers or wires on the floor or uses vision, magnets, or lasers for navigation. They are most often used in industrial applications to move materials around a manufacturing facility or warehouse.
Name fusion welding processes
- Manual Metal Arc (MMA)
- Submerged arc welding (SAW)
- Metal inert gas (MIG)
- Tungsten inert gas (TIG)
- Laser
- Electron beam
Significance of re-crystalline temperature
Recrystallization is a process by which deformed grains are replaced by a new set of defects-free grains that nucleate and grow until the original grains have been entirely consumed. Recrystallization is usually accompanied by a reduction in the strength and hairiness of a material and a simultaneous increase in ductility. Thus, the process may be introduced as a deliberate step in metals processing or may be an undesirable by-product of another processing step. The most important industrial uses are the softening of metals) previously hardened by cold work, which has lost their ductility, and the control of the grain structure in the final product.
Function of cores
A core is a device used in casting and moulding processes to produce internal cavities and re-entrant angles. The core is normally a disposable item that is destroyed to get it out of the piece. They are most commonly used in sand casting but are also used in injection m|oulding.
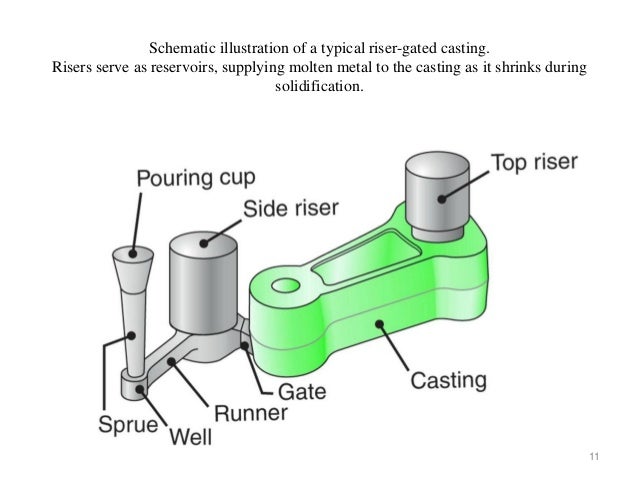
Function of risers
A riser, also known as a feeder, is a reservoir built into a metal casting mould to prevent cavities due to shrinkage. Most metals are less dense as a liquid than as a solid so castings shrink upon cooling, which can leave a void at the last point to solidify. Risers prevent this by providing molten metal to the casting as it solidifies so that the cavity forms in the riser and not the casting.
CAPP
Computer-aided process planning (CAPP) is the use of computer technology to aid in the process planning of a part or product, in manufacturing. CAPP is the link between CAD and CAM in that it provides for the planning of the process to be used in producing a designed part.
Soldering
Soldering: Soldering. is a process in which two or more items (usually metal) are joined together by melting and putting a filler metal (solder) into the joint, the filler metal having a lower melting point than the adjoining metal. Soldering differs from welding in that soldering does not involve melting the workpieces.
Design by evolution
Design by evolution: In the past, the designs tended to evolve over long spans of time. The development pace was slow. Devices/products were static for quite some time. The changes were small and gradual. Each change made a small improvement in the preceding model. Such a situation is referred to as design by evolution in which technical risk and stakes are proportionally small.
Problem identification
A problem occurs when there is a difference between what "should be" and what "is" and when the resulting situation is regarded as unwelcome and needs to be overcome. Einstein is quoted as having said that if he had one hour to save the world he would spend fifty-five minutes defining the problem and only five minutes finding the solution. Identifying a very clearly defined and specific problem is the first critical step to successfully implementing the problem-solving process.
Design morphology
Morphology means ‘a study of form or structure’. Morphology of design refers to the time-based sequencing of design operations. It is a methodology of design by which ideas about things are converted into physical objects. The logical order of different activities or phases in a design project is called the morphology of design.
---
The study material for AMIE/B Tech/Junior Engineer exams is available at https://amiestudycircle.com



Comments