Short answer type (2 x 4)
Find the dimension of Torque in the SI unit of the M, L, T, I system.
Dimension formula of torque = dimension formula of force X dimension formula of length
[MLT-2][L]=[ML2T-2]
Find the equivalent resistance of series connected two resistances R₁ = 40 ± 2% and R₂ = 60 ± 3%.
R1 + R2 = 40 ± 2 + 60 ± 3 = 100 ±5%
Write the type and order of a system whose transfer function is given by
Order of the system can be defined as the value of the highest exponent that appears in the denominator of the transfer function. (Total number of poles). In the given expression highest exponent is 3. Hence the order of the system is 3.
Find the no. of significant figures in
(a) 0.0012
(b) 12.00
(c) 1200
(d) 12
0.0012 has 2 significant figures.
12.00 has 4 significant figures.
1200 has 2 significant figures.
12 has 2 significant figures.
Significant figures are the digits of a number that are meaningful in terms of accuracy or precision. They include:
- Any non-zero digit
- Zeros between non-zero digits as in 3003 or 45.60009
- Trailing zeros only when there is a decimal point as in 6750. or 274.3300
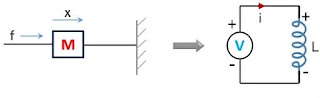
Force voltage analogy
Consider the following figure.
Mechanical system
The element ‘mass’ in the mechanical system corresponds to an inductor in the electrical network.
where x represents the amount of displacement and v is the velocity.
Electrical network
Uses of Wien’s bridge method
Following are some of the important applications of the Wien bridge that are important from the subject point of view:
- 1. This bridge is used for measuring the frequency in the audio range.
- 2. The Wien bridge is used in audio and HF oscillators as the frequency-determining device.
- 3. The bridge is used in a harmonic distortion analyser, as a notch filter, and an audio frequency and radio frequency oscillators as a frequency-determining element.
Absolute stability and relative stability
Relative stability
It is measure of how fast the transient dies out in the system .relative stability is related to settling time. a system having poles away from the left half of imaginary axis is considered to be relatively more stable compared to a system having poles closed to imaginary axis.
The relative stability may be found by shifting the imaginary axis to the left by some constant amount σ. This can be easily done by replacing s with s + σ in the characteristic equation and applying the Routh-Hurwitz criteria.
Absolute stability
If the system returns to its equilibrium state after the inputs given to the system are removed. Routh’s stability criterion provides information about absolute stability.
- The study material for AMIE/B Tech/Junior Engineer exams is available at https://amiestudycircle.com
- If you like the post please share your thoughts in the comment section
Comments