Answer any four in brief (4 x 5)
Final value theorem with example
In the solution of Networks, Transient, and Systems sometimes we may not be interested in finding out the entire function of time f(t) from its Laplace Transform F(s), which is available for the solution. It is very interesting to find that we can find the first value or last value of f(t) or its derivatives without having to find out the entire function f(t).
If F(s) is given, we would like to know what is F(∞), Without knowing the function f(t), which is Inverse Laplace Transformation, at time t → ∞. This can be done by using the property of Laplace Transform known as the Final Value Theorem. The final value theorem and initial value theorem are together called the Limiting Theorems.
If f(t) and f'(t) both are Laplace Transformable and sF(s) has no pole in jw axis and in the R.H.P. (Right half Plane) then,
Z parameters in terms of ABCD parameters
Properties of Hurwitz polynomial
If above all the stability criteria are fulfilled (i.e. we have a stable network function) then the denominator of the F(s) is called the Hurwitz polynomial.
Where Q(s) is a Hurwitz polynomial.
There are five important properties of Hurwitz polynomials and they are written below:
- For all real values of s value of the function P(s) should be real.
- The real part of every root should be either zero or negative.
- Let us consider the coefficients of the denominator of F(s) is bn, b(n - 1), b (n - 2). . . . b0. Here it should be noted that bn, b(n-1), b0 must be positive and bn and b(n-1) should not be equal to zero simultaneously.
- The continued fraction expansion of even to the odd part of the Hurwitz polynomial should give all positive quotient terms, if even degree is higher or the continued fraction expansion of odd to the even part of the Hurwitz polynomial should give all positive quotient terms, if odd degree is higher.
- In the case of purely even or purely odd polynomial, we must do continued fraction with the derivative of the purely even or purely odd polynomial and the rest of the procedure is the same as mentioned in the point number (4).
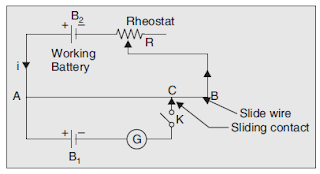
Potentiometer
A potentiometer is an instrument used for measuring and comparing the emfs of different cells and for calibrating and standardizing voltmeters, ammeters etc. It is a device used for the measurement of
unknown emf by comparison. The unknown emf is compared with a known emf which is obtained
from a standard cell or any reference voltage source.
A potentiometer is a three-terminal resistor with a sliding contact that forms an adjustable
voltage divider. If only two terminals are used, it acts as a variable resistor or rheostat. Potentiometers
are commonly used to control electrical devices such as volume controls on audio equipment.
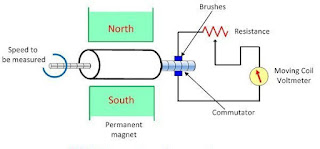
Purpose of tachogenerator
Tachogenerators are electromechanical devices that output a voltage proportional to their shaft speed. They are used to power tachometers and to measure the speed of motors, engines, and other rotational devices.
What is frequency transformation?
Frequency transformation techniques are used to generate a High pass filter, Bandpass and bandstop filter from the lowpass filter system function.
Once you use a frequency transformation in filter design, you can apply standard simulation tools to examine electrical behaviour for your filter stages and analog circuit networks.
---
- The study material for AMIE/B Tech/Junior Engineer exams is available at https://amiestudycircle.com
- If you like the post please share your thoughts in the comment section

Comments