Choose the correct answer (2 x 10)
1. The internal RAM memory of the 8051 is
(a) 32 bytes
(b) 64 bytes
(c) 128 bytes
(d) 256 bytes
2. This program code will be executed continuously:
STAT: MOV A, #01H
JNZ STAT
(a) True
(b) False
3. The 8051 has ------16-bit counter/timers.
(a) 1
(b) 2
(c) 3
(d) 4
4. The address space of the 8051 is divided into four distinct areas: internal data, external data, internal code, and external code.
(a) True
(b) False
5. In the 8086 microprocessor, the address bus is a ---- bit wide
(a) 12
(b) 10
(c) 16
(d) 20
6. The 1 MB of memory can be divided into ---------- segment
(a) 1 Kbyte
(b) 64 Kbyte
(c) 33 Kbyte
(d) 34 Kbyte
7. In 8086 BIU stands for -------
8. Which of the following 8085 interrupts is nonmaskable?
(a) RST 7.5
(b) INTR
(c) RST 6.5
(d) TRAP
9. Which of the following interrupt is a non vectored interrupt?
(a) RST7.5
(b) INTR
(c) RST6.5
(d) TRAP
10. Maximum size of memory for 8085 microprocessor
(a) 1 MB
(b) 16 KB
(c) 64 KB
(d) 32 KB
Answers
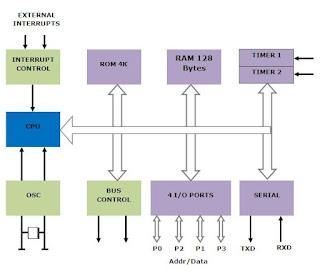
1. (c) 8051 is an 8-bit microcontroller built with 40 pins DIP (dual inline package). 8051 has internal RAM (128 Bytes) and ROM (4K Bytes). Of the 128-byte internal RAM, only 16 bytes are a bit-addressable. The rest must be accessed in byte format.
3. (b) The 8051 has two timers, Timer 0 and Timer 1. They can be used as timers or as event counters. Both Timer 0 and Timer 1 are 16-bit wide. Since the 8051 follows an 8-bit architecture, each 16 bit is accessed as two separate registers of low-byte and high-byte.
4. (a)
5. (d)
6. (b) The 8086 architecture uses the concept of segmented memory. 8086 is able to address a memory capacity of 1 megabyte and it is byte organized. This 1-megabyte memory is divided into 16 logical segments. Each segment contains 64 Kbytes of memory.
7. Bus Interface Unit. The execution unit of the 8086 tells the BIU where to fetch instructions or data from, decodes instructions, and executes instructions
8. (d)
- Maskable Interrupts are those which can be disabled or ignored by the microprocessor. These interrupts are either edge-triggered or level-triggered, so they can be disabled. INTR, RST 7.5, RST 6.5, RST 5.5 are maskable interrupts in the 8085 microprocessors.
- Non-Maskable Interrupts are those which cannot be disabled or ignored by microprocessors. TRAP is a non-maskable interrupt. It consists of both level as well as edge triggering and is used in critical power failure conditions.
9. (b)
- Non-Vectored Interrupts are those in which vector address is not predefined. The interrupting device gives the address of sub-routine for these interrupts. INTR is the only non-vectored interrupt in the 8085 microprocessor. Generally, it uses the address of software interrupts i.e. RST 0 to RST 7.
- Vectored Interrupts are those which have fixed vector addresses (starting address of sub-routine) and after executing these, program control is transferred to that address.
10. (c) 8085 can access up to 64Kb, whereas 8086 can access up to 1 Mb of memory.
---
- The study material for AMIE/B Tech/Junior Engineer exams is available at https://amiestudycircle.com
- If you like the post please share your thoughts in the comment section
Comments