Answer the following (2 x 10)
Tool life can be almost infinite at low cutting speeds. Would you then recommend that all matching be done at low speeds? Explain.
This reason alone would not justify using low cutting speeds. Low cutting speeds remove less material in a given time which, unless otherwise justified, would be economically undesirable. Lower cutting speeds also often lead to the formation of a built-up edge and discontinuous chips, thus affecting the surface finish.
Which tool material properties are suitable for interrupted cutting operations? Why?
In interrupted cutting operations, it is desirable to have tools with a high impact strength and toughness. The tool materials which have the best impact strength are high-speed steels, and to a lesser extent, cast alloys and carbides. Therefore, one would prefer to use high-speed steels and carbides in interrupted cutting operations. In addition, in these operations, the tool is constantly heated and reheated. It is therefore desirable to utilize materials with low coefficients of thermal expansion and high thermal conductivity to minimize thermal stresses in the tool which could lead to tool failure.
Can cutting fluids have any adverse effects on machining? If so, what are they?
Cutting fluids can have adverse effects on the freshly machined surfaces, as well as various components of the machine tool and the lubricants used on the machines themselves, such as altering their viscosity and lubricating capabilities.
If a cutting fluid is very effective as a coolant, it could lead to thermal shock in interrupted cutting operations.
Cutting fluids have to be replaced periodically because they degrade, adversely affecting their performance. This degradation can be due to intense shear in the cutting zone, contamination by other materials, or bacteria attacking the oil (or, more commonly, the emulsifier).
If the cutting is no longer effective because of this degradation, workpiece quality will be compromised, but then there is the additional environmental concern associated with fluid disposal.
During the occurrence of crater wear and flank wear, there is a change in cutting force. Explain whether it will increase or decrease and why.
Crater wear can increase the working rake angle and reduce the cutting force, but it will also weaken the strength of the cutting edge.
What is the Bauschinger effect?
The Bauschinger effect is the phenomenon by which plastic deformation of a metal increases the yield strength in the direction of plastic flow and decreases the yield strength in the opposite direction.
What is isotropic strain hardening?
In isotropic hardening, the yield surface increase in size, but remain the same shape, as a result of plastic straining. That is, if the yield surface is represented by a cylinder of radius "A" then an increase in the radius denotes an increase in the yield stress as a result of plastic straining.
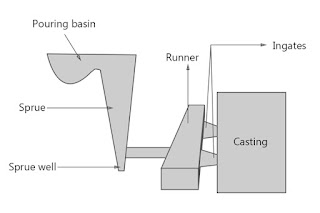
What is the choke area in the sand casting mould?
Ingate (also known as choke area) is the portion in the gating system which is present between the sprue base and mould cavity. The molten metal has to pass through the ingate area in order to enter the inner area of the mould. It is the minimum area of the gating system which meters the flow of molten metal into the mould cavity.
What is a pressurised gating system?
The Pressurized gating system is a gating system whose cross-sectional surface area decreases gradually towards the mould cavity. The in-gate area is minimized to put pressure on the system.
What is open circuit voltage (OCV) in welding?
Open Circuit Voltage (also known as no-load voltage) is the voltage that exists between the electrode and the job (or the earth) when welding is not in progress.
---
The study material for AMIE/Junior Engineer exams is available at https://amiestudycircle.com
Comments