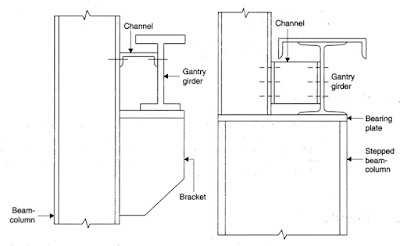
Explain various components of gantry girder through neat sketches.
- The web plate
- Flange plate (addition of cover plate curtailed at proper sections)
- Stiffeners like bearing stiffeners, longitudinal stiffeners, and intermediate stiffeners
- Splices for flange plate and web plate
- End connections
Advantages of HSFG bolts over bearing bolts.
- Whereas the rivets are subjected to shear and bearing stresses, the bolts are subjected to uniform tensile stresses only.
- The high strength friction grip bolts have higher fatigue strength because there is no concentration of the stress in the hole.
- The bolts do not bear against the plates. Therefore, the uneven distribution of stress does not occur.
- These bolts are advantageously used in bridges and machine foundations subjected to vibrations.
- These bolts also simplify the problem of alterations and additions to structures as they can be assembled more easily than rivets.
Discuss wind load calculation for design of roof truss.
Enlist advantages of bolted connections over riveted connections.
- There is silence in preparing bolted connection. In riveting, hammering is done. The hammering causes noise in the riveting.
- There is no risk of fire in bolted connection. The rivets are made red hot in riveting and there is a risk of fire.
- The bolted connections may be done quickly in comparison to the riveting.
- Though the cost of bolts is more than the cost of rivets, the bolted connections are economical to use than rivets because fewer persons are required for installation, and the work proceeds quickly.
- The bolted connections facilitate the erection because of the ease with which these connections can be done.
- If bolted connections become loose, their strength reduces considerably.
- Tire unfinished bolts are not uniform in diameter and they have less strength.
- The bolted connections have less strength when they are subjected to axial tension because the area at the root of the thread is less.
- Generally, the diameter of the hole is kept 16 mm more than the nominal diameter of the black bolt. The bolt does not fill the hole and there remains a clearance in bolted connections.
- A riveted joint is more reliable than welded joints in applications which are subjected to vibrations and impact forces.
- Riveted joints can be used for non-ferrous metals like aluminium alloy, copper, brass or even non-metal like plastic and asbestos.
- Riveted joints are free from thermal after-effects because no heat required in this joint.
- Quality inspection is easy in a riveted joint.
- When the riveted joint is dismantled, the connected components are less damaged as compared to a welded joint.
- The material cost of a riveted joint is more.
- The labour cost of riveted joints is also more than that of the welded joint.
- Overall cost if the riveted joint is also high.
- The riveted assembly has more weight than the welded assembly.
- The riveting process creates more noise because of hammer blows.
- Holes required to insert rivets cause stress concentration.
- Production time is more for assembly.
- Riveted assemblies are not tight and leak proof.
- The projection of the riveted head adversely affects the appearance of the riveted structure.
State indeterminacy with example of a beam, truss and frame.
A Statically Indeterminate structure can be said if the equilibrium equation is insufficient for finding the structure's unknowns. These unknowns can be the Deformation, Support reaction, Shear force, bending moment, etc. For analysing such a structure, there is a need for some special equations called compatibility equations.
Statically indeterminate beams are the beams that require compatibility conditions along with available equilibrium equations for their analysis. Compatibility conditions of beams depend on the support conditions and type of loading etc. Compatibility conditions are based on the internal structure of the beams, like deformations and slopes of the beam. Fixed beams, propped cantilever beams, Continuous beams, etc., are examples of indeterminate beams.
Statically indeterminate frames/trusses are the frames that require some compatibility conditions for their analysis. Compatibility conditions of frames include horizontal deflection, the slope of supports, etc.

Comments