Answer the following in brief (2 x 10)
What is the difference between linear and nonlinear systems?
A control system is known as linear if it satisfies the additive property as well as the homogeneous property.
Additive Property: If x and y belong to the domain of the function f, we can write
f(x + y) = f(x) + f(y)
Homogeneous Property: For any x belonging to the domain of the function f and for any scalar constant α, we can write
f(αx) = αf(x)
The principle of superposition is a combination of the above two properties. If a function satisfies the above two properties, it is said to be linear in nature.
If f(x) = x3, it is obvious that f(x + y) = (x + y)3 ≠ x3 + y3 and f(αx) = (αx)3 = α3x3 # α(x)3. Therefore the function f(x) = x3 is non-linear.
Explain the working standards in the measurement system.
Working Standards Working standards are the principal tools of a measurement laboratory. They are used to check laboratory instruments for accuracy and performance. These standards are used to perform comparison measurements in industrial applications. For example, manufacturers of components such as capacitors, resistors etc. use a standard called a working standard for checking the
component values being manufactured, e.g. a standard capacitor for checking of capacitance value
manufactured.
Explain the term ‘Instrumental error’.
Instrumental Errors The instrument error generate due to the instrument itself. It is due to the inherent shortcomings in the instruments, misuse of the instruments, loading effects of instruments. For example in the D’ Arsonval movement friction in bearings of various moving components may cause incorrect
readings. There are so many kinds of instrument errors, depending on the type of instrument used.
Instrumental errors may be avoided by
- Selecting a suitable instrument for the particular measurement application
- Applying correction factors after determining the amount of instrumental error
- Calibrating the instruments against a standard.
Give one example of the closed-loop control system.
If controlling actions of a system is dependent on output or changes in output, the system is called a closed-loop system. The following figure depicts a closed-loop system.
Write any two advantages electrical/electronic Instruments.
- Different physical quantities can be converted into an electrical signal by transducers.
- The electrical signal can be amplified, multiplexed, filtered and measured easily.
- The electrical signals can be converted from A/D or D/A signals.
- Electrical signals can be transmitted over long distances by wire or radio link etc.
- Many measurements can be carried out simultaneously.
- Digital signals are compatible with computers.
- High Sensitivity, low power consumption, high reliability.
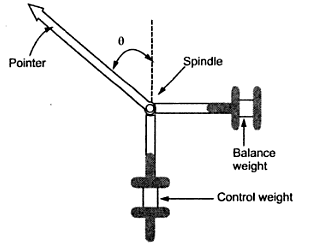
Compare the spring control and Gravity control.
- In gravity control, an adjustable small weight is used which produces the controlling torque. In spring control, two hairsprings are used which exert controlling torque.
- Controlling torque can be varied in gravity control whereas controlling torque is fixed in spring.
- In gravity, the performance is not temperature-dependent while in the spring the performance is temperature-dependent.
- The scale is nonuniform in gravity. The scale is uniform in spring control.
- The controlling torque is proportional to sin(angle) in the first whereas, in the second, the controlling torque is proportional to the angle.
- The readings can not be taken accurately in the gravity. The readings can be taken very accurately in the spring.
- The system must be used in vertical position only in gravity control. The system need not be necessarily in a vertical position in spring control.
- Proper levelling is required as gravity control. The levelling is not required.
Spring control
Gravity control
List any two characteristics of the potentiometer.
- The potentiometer is very accurate because its works on the comparing method rather than the deflection pointer method for determining the unknown voltages.
- It measures the null or balance point which does not require power for the measurement.
- The working of the potentiometer is free from the source resistance because no current flows through the potentiometer when it is balanced.
Write any two basic requirements for an oscillatory circuit.
- The oscillator requires amplification to provide the necessary gain for the signal
- To sustain oscillations, the oscillator requires sufficient regenerative feedback.
Write the expression for electrostatic deflection.
where
Va = Accelerating voltage
d = distance between Y plates
l = length of each Y plates
D = distance from point O to screen
Vd = Deflecting voltage
yab = Deflection on the screen
What is the difference between a wattmeter and an energy meter?
- The energy meter measures the total energy consumed by the load while the wattmeter measures the power in a circuit.
- The energy meter measures the energy in joules but wattmeter the measure the power in watts.
- The energy meter driving, braking, and moving system along with the counting mechanism are the main parts, but the wattmeter pressure and current coil, control system, scale and pointer, damping system to the central part.
- The energy meter work on the principle of conversion of electrical energy into mechanical energy. Whereas the wattmeter works on the principle that the force acts on the current-carrying conductor when it is placed in an electromagnetic field.
- The energy meter is used for measuring the total power consumed by the load in the industries and homes while the wattmeter is used for measuring the power of an electrical circuit. It is also used for determining the power rating of homes and industrial appliances.
---
- The study material for AMIE/B Tech/Junior Engineer exams is available at https://amiestudycircle.com
- If you like the post please share your thoughts in the comment section


Comments